NOVEMBER IS NATIONAL DIABETES MONTH

| Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood glucose. Symptoms Symptoms of diabetes may occur suddenly. In type 2 diabetes, the symptoms can be mild and may take many years to be noticed. Symptoms of diabetes include: 1) Feeling very thirsty 2) Needing to urinate more often than usual 3) Blurred vision 4) Feeling tired 5) Losing weight unintentionally Over time, diabetes can damage blood vessels in the heart, eyes, kidneys and nerves. People with diabetes have a higher risk of health problems including heart attack, stroke and kidney failure. It can cause permanent vision loss by damaging blood vessels in the eyes. Many people with diabetes also can develop problems with their feet from nerve damage and poor blood flow. This can cause foot ulcers and may lead to amputation. |

| Prevention Lifestyle changes are the best way to prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes. To help prevent type 2 diabetes and its complications, people should: 1) Reach and keep a health body weight 2) Stay physically active with at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise each day 3) Eat healthy and avoid sugar and saturated fat 4) Not smoke tobacco. Diagnosis and treatment Early diagnosis can be accomplished through relatively inexpensive testing of blood glucose. People with type 1 diabetes need insulin injections. One of the most important ways to treat diabetes is to keep a healthy lifestyle. Some people with type 2 diabetes will need to take medicines to help manage their blood sugar levels. These can include insulin injections or other medicines. Along with medicines to lower blood sugar, people with diabetes often need medications to lower their blood pressure and statins to reduce the risk of complications. Additional medical care may be needed to treat the effects of diabetes such as: 1) Foot care to treat ulcers 2) Screening and treatment for kidney disease 3) Eye exams to screen for retinopathy (which can cause blindness). |
| If you are suffering from some or all of the symptoms above, call us to schedule your check up. We can help you live a healthier, happier life. |
WHAT IS COPD?
| What Should You Know: |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) makes it feel like there’s something continually blocking the pathway to your lungs, making it hard to breathe. Although it’s considered a disease in itself, COPD is also an umbrella term that incorporates several other breathing-related conditions, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis. |
Types of COPD
Let’s take a closer look at how your breathing is compromised with the two most common forms of COPD:
Emphysema
When the walls of the alveoli break down, instead of having a bunch of little air sacs, one sac leaches into the next, and you end up with fewer, larger, air sacs. The problem with these larger sacs is that there is less overall surface capacity for oxygen to reach your bloodstream. Plus, the airways throughout the lungs can lose their stretchiness, trapping air inside, which is why emphysema causes shortness of breath.
Chronic Bronchitis
When the bronchial tubes become inflamed or irritated, it can lead to coughing and feeling short of breath. The duration of the bronchitis is important. If you’re coughing and producing mucus at least three months at a time for two years in a row, it’s considered chronic bronchitis, a type of COPD that is treatable, but not fully reversible.
How serious are these breathing problems? Well, COPD is the fourth leading cause of death in the U.S. More than 16.4 million people have been diagnosed with COPD, although experts believe the true number is much higher (many people don’t seek help until the disease has advanced). Let’s take a closer look at what’s behind this chronic lung condition.
What Causes COPD?
For the majority of Americans, COPD is the result of cigarette smoking. The remaining 25 percent of people can attribute it to air pollution, mainly second hand smoke and chemical fumes. Some asthma sufferers are also diagnosed with COPD. In this case, treatment can usually reverse the inflammation that causes narrowing in the lung’s airways.
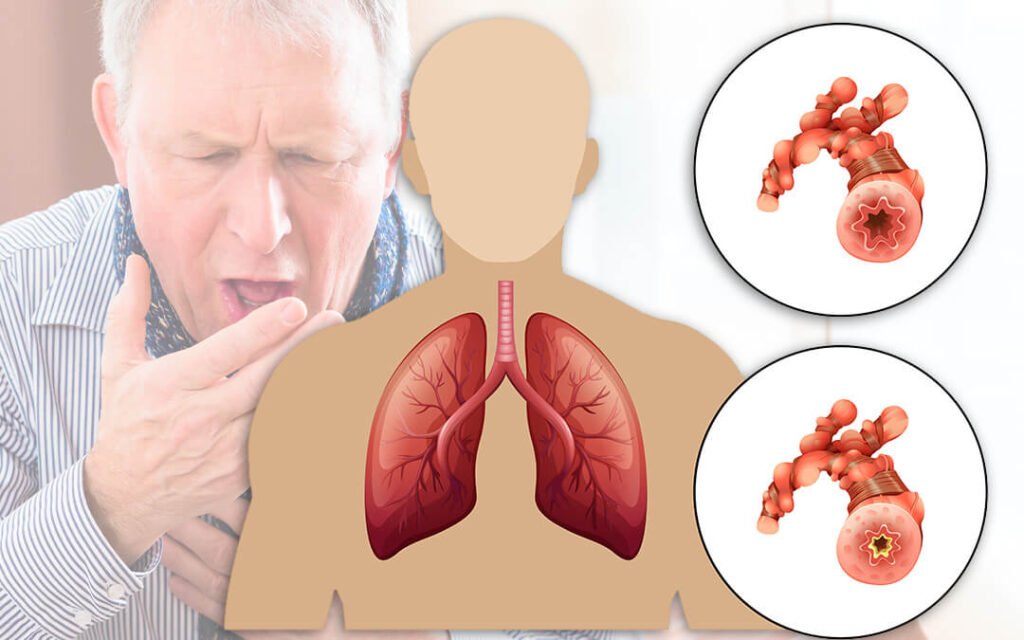
SYMPTOMS
With so many broad symptoms, perhaps it’s not surprising that COPD is often misdiagnosed. Along with a lingering cough, if any of the symptoms below describes your situation, make an appointment to see your doctor. He may then refer you to a pulmonologist. The most common signs of COPD include:
- Chest tightness
- Chronic coughing—sometimes producing mucus, sometimes not
- Fatigue
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Increased shortness of breath
- Wheezing
If you are experiencing COPD symptoms, you should not be afraid or ashamed. You’re one of millions of Americans in the same boat. There are many treatment options and combinations of drugs. Once you receive the proper diagnosis, you and your doctor can figure out a plan to improve your health and quality of life.
A GUIDE TO LIVING YOUR BEST LIFE

Get regular check ups
It’s important to have a good relationship with a primary doctor and to have regular check ups to make sure that you remain in good health or have the tools you need to manage any health issues you have or will develop.
Eat a balanced diet
Eating a balanced diet is essential for your health. It’s important to eat a variety of nutrient-dense foods to ensure you’re getting all the essential vitamins and minerals your body needs. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats in your diet.
Exercise regularly
Exercise to maintain a healthy weight. It can reduce the risk of chronic disease, and improving overall mental health. Aim for 20-30 minutes of moderate intensity exercise most days of the week. Perhaps you would enjoy walking, cycling, or swimming.
Get enough sleep
Getting enough sleep helps with your physical and mental health. You should get 7–9 hours of sleep per night. Having a consistent sleep routine, avoiding too much caffeine and electronics before bed, and creating a comfortable sleep environment can help improve sleep quality.
Manage stress
Chronic stress can have detrimental effects on both physical and mental health. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature. It’s also essential to take breaks and prioritize self-care to prevent burnout.
Avoid harmful habits
Harmful habits like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use can have many negative effects on physical and mental health. Quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, and avoiding drug use can help prevent a range of chronic diseases and improve overall health.
Living a healthy lifestyle involves a combination of a balanced diet, moderate exercise, adequate sleep, stress management, and avoiding harmful habits. Making small, changes can lead to improvements in physical and mental health over time. Prioritizing self-care and seeking support from healthcare professionals can also help maintain optimal health.
